What is bereavement?
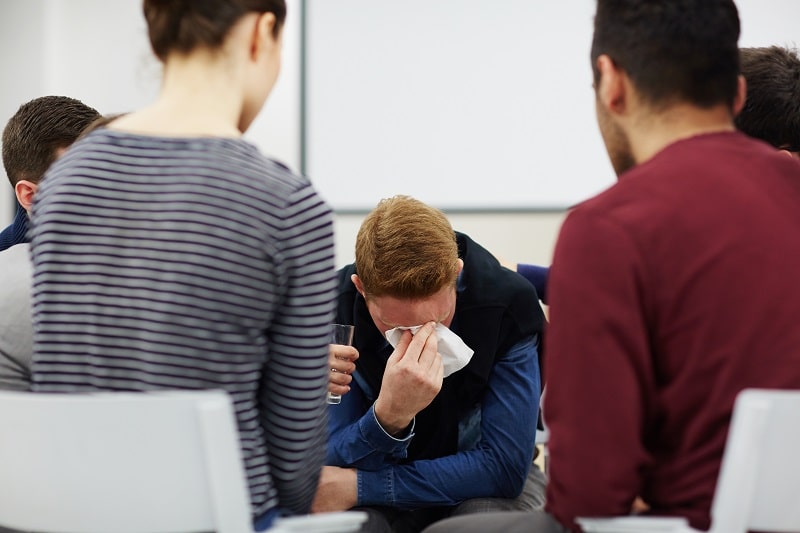
Bereavement is the grief and mourning experience following the death of someone important to you. While it’s an inevitable part of life—something that virtually all of us go through at some point—losing someone you love can be one of the most painful experiences you’ll ever have to endure.
Whether it’s a close friend, spouse, partner, parent, child, or other relative, the death of a loved one can feel overwhelming. You may experience waves of intense and very difficult emotions, ranging from profound sadness, emptiness and despair, to shock, numbness, guilt, or regret. You might rage at the circumstances of your loved one’s death—your anger focused on yourself, doctors, other loved ones, or God. You may even find it difficult to accept the person is really gone, or struggle to see how you can ever recover and move on from your loss.
Bereavement isn’t limited to emotional responses, either. Grief at the death of a loved one can also trigger physical reactions, including weight and appetite changes, difficulty sleeping, aches and pains, and an impaired immune system leading to illness and other health problems.
The level of support you have around you, your personality, and your own levels of health and well-being can all play a role in how grief impacts you following bereavement. But no matter how much pain you’re in right now, it’s important to know that there are healthy ways to cope with the anguish and come to terms with your grief. While life may never be quite the same again, in time you can ease your sorrow, start to look to the future with hope and optimism, and eventually move forward with your life.
Understanding the grief of losing a loved one
The intensity of your feelings often depends on the circumstances of your loved one’s death, how much time you spent anticipating their loss, your relationship to them, and your previous experiences of bereavement. Of course, just as no two relationships are the same, no two losses are ever the same, either.
In short, the more significant the person was in your life and the more feelings you had for them—regardless of their relationship to you—the greater the impact their loss is likely to have.
Losing a spouse or partner
In addition to the emotional impact of grief, when you lose a spouse or romantic partner, you often must deal with the stress of practical considerations such as funeral arrangements and financial issues, too. You may also have to explain your spouse’s death to your children and find a way to comfort them while simultaneously dealing with your own heartache.
Losing a romantic partner also means grieving the loss of your daily lifestyle, the loss of a shared history, and the loss of a future planned together. You may feel alone, despairing, and worried about the future. You could even feel guilty about somehow having failed to protect your partner, or angry at your loved one for leaving you.
Losing a parent
For younger children, losing a mother or father can be one of the most traumatic things that can happen in childhood. The death of the person you relied on, the person who loved you unconditionally, can shake your foundations and leave a huge, frightening void in your world. It’s also common for young children to blame themselves for a parent’s death, prolonging the pain of grief.
Even as an adult child, losing a parent can be extremely distressing. It’s easy to feel lost and for all those old childhood insecurities to suddenly return. You may gain some solace if your parent had a long and fulfilling life, but their death can also cause you to consider your own mortality. If you’ve lost both parents, you’re suddenly part of the older generation, a generation without parents, and you’re left to grieve your youth as well. And if your relationship with your parent wasn’t an easy one, their death can leave you wrestling with a host of conflicting emotions.
Losing a child
The loss of a child is always devastating. You’re not just losing the person they were, you’re also losing the years of promise, hopes, and dreams that lay ahead. The grief can be more intense, the bereavement process harder to navigate, and the trauma more acute.
As a parent, you feel responsible for your child’s health and safety, so the sense of guilt can often be overwhelming. Whether you lost your child in a miscarriage, as an infant, or after they’d grown up and left home, losing a child carries an additional weight of injustice. It feels unnatural for a parent to outlive their child, making it that much harder to find meaning and come to terms with their death.
Losing a child can also put a huge strain on your relationship with your spouse or partner and make parenting any surviving children emotionally challenging.
Losing a friend
Close friendships bring joy, understanding, and companionship into our lives. In fact, they’re vital to our health and well-being, so it’s no wonder we can feel their loss so gravely.
When a close friend dies, though, it’s easy to feel marginalised, the closeness of your relationship not given the same significance as a family member or romantic partner. This can lead to what’s called disenfranchised grief, where your loss is devalued, or you feel judged or stigmatised for feeling the loss so deeply.
Losing someone to suicide
The shock following a suicide can seem overwhelming. As well as mourning the loss of your loved one, you may also be struggling to come to terms with the nature of their death and the stigma that suicide can still carry.
While you may always be left with some unanswered questions about your loved one’s suicide, there are ways to resolve your grief and even gain some level of acceptance.
Grieving your loss
Whatever your relationship to the person who died, it’s important to remember that we all grieve in different ways. There’s no single way to react. When you lose someone important in your life, it’s okay to feel how you feel. Some people express their pain by crying, others never shed a tear—but that doesn’t mean they feel the loss any less.
Don’t judge yourself, think that you should be behaving in a different way, or try to impose a timetable on your grief. Grieving someone’s death takes time. For some people, that time is measured in weeks or months, for others it’s in years.
Allow yourself to feel. The bereavement and mourning process can trigger many intense and unexpected emotions. But the pain of your grief won’t go away faster if you ignore it. In fact, trying to do so may only make things worse in the long run. To eventually find a way to come to terms with your loss, you’ll need to actively face the pain. As bereavement counsellor and writer Earl Grollman put it, “The only cure for grief is to grieve.”
Prepare for painful reminders. Some days the pain of your bereavement may seem more manageable than others. Then a reminder such as a photo, a piece of music, or a simple memory can trigger a wave of painful emotions again. While you can’t plan for such reminders, you can be prepared for an upcoming holiday, anniversary, or birthday that may reignite your grief. Talk to other friends and family ahead of time and agree on the best ways to mark such occasions.
Moving on doesn’t mean forgetting your loved one. Finding a way to continue forward with your life doesn’t mean your pain will end or your loved one will be forgotten. Most of us carry our losses with us throughout life; they become part of who we are. The pain should gradually become easier to bear, but the memories and the love you had for the person will always remain.
Seek support
When you lose someone you love, it’s normal to want to cut yourself off from others and retreat into your shell. But this is no time to be alone. Even when you don’t feel able to talk about your loss, simply being around other people who care about you can provide comfort and help ease the burden of bereavement.
Reaching out to those who care about you can also be an important first step on the road to healing. While some friends and relatives may be uncomfortable with your grief, plenty of others will be eager to lend support. Talking about your thoughts and feelings won’t make you a burden. Rather, it can help you make sense of your loved one’s death and find ways to honour their memory.
Lean on friends and family. Even those closest to you can struggle to know how to help during a time of bereavement, so don’t hesitate to tell others what you need—whether it’s helping with funeral arrangements or just being around to talk. If you don’t feel you have anyone you can lean on for support at this difficult time, look to widen your social network and build new friendships.
Focus on those who are “good listeners”. When you’re grieving the loss of a close friend or family member, the most important thing is to feel heard by those you confide in. But the raw emotion of your grief can make some people very uncomfortable. That discomfort can cause them to avoid you, say thoughtless or hurtful things, or lose patience when you talk about your loss. Don’t use their actions as a reason to isolate, though. Turn to those who are better able to listen and provide comfort.
Join a bereavement support group. Even when you have support from those closest to you, family and friends may not always know the best ways to help. Sharing your grief with others who have experienced similar losses can help you feel less alone in your pain. By listening to others share their stories, you can also gain valuable coping tips. To find a support group in your area, contact nearby hospitals, funeral homes, or counselling centres, or call a bereavement hotline listed below.
Talk to a bereavement counsellor. If you’re struggling to accept your loss or your grief feels overwhelming, try talking to a bereavement or grief therapist—in-person or via video conferencing online. Confiding in a professional can help you work through emotions that may be too difficult to share with family or friends, deal with any unresolved issues from your loved one’s death, and find healthier ways to adapt to life following your loss.
Draw comfort from your religion. If you’re religious, the specific mourning rituals of your faith can provide comfort and draw you together with others to share your grief. Attending religious services, reading spiritual texts, praying, meditating, or talking to a clergy member can also offer great comfort and help you derive meaning from your loved one’s death.
Take care of yourself
When you’re grieving the death of a loved one, it’s easy to neglect your own health and welfare. But the stress, trauma, and intense emotions you’re dealing with at that moment can impact your immune system, affect your diet and sleep, and take a heavy toll on your overall mental and physical health.
Neglecting your well-being may even prolong the grieving process and make you more susceptible to depression or complicated grief. You’ll also find it harder to provide comfort to children or other vulnerable family members who are also grieving. However, there are simple steps you can take to nurture your health at this time.
Manage stress. It’s probably the last thing you feel like doing at that moment, but exercising is a powerful antidote to stress—and can help you sleep better at night. Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga are also effective ways to ease anguish and worry.
Spend time in nature. Immersing yourself in nature and spending time in green spaces can be a calming, soothing experience when you’re grieving. Try gardening, hiking, or walking in a park or woodland.
Pursue interests that enrich your life. Hobbies, sports, and other interests that add meaning and purpose to your life can bring a comforting routine back to your life following the upheaval of bereavement. They can also help connect you with others and nurture your spirit.
Eat and sleep well. Eating a healthy diet and getting enough rest at night can have a huge impact on your ability to cope with grief. If you’re struggling to sleep at this difficult time, there are supplements and sleep aids that may be able to help—just try not to rely on them for too long.
Avoid using alcohol or drugs to cope. While it’s tempting to use substances to help numb your grief and self-medicate your pain, in the long run excessive alcohol and drug use will only hamper your ability to grieve.
When the pain of bereavement doesn’t ease up
You may never truly get over the death of someone you love. But as time passes, it’s normal for difficult emotions such as sadness or anger to gradually ease as you begin to accept your loss and move forward with your life.
However, if you aren’t feeling better over time, or your pain is getting worse, it may be a sign that your grief has developed into a more serious problem, such as complicated grief or major depression.
Grief vs. depression
Distinguishing between grief and depression isn’t always easy as they share many symptoms, but there are ways to tell the difference:
- Grief can be a roller coaster. It involves a wide variety of emotions and a mix of good and bad days. Even when you’re in the middle of the grieving process, you will still have moments of pleasure or happiness.
- With depression, on the other hand, the feelings of emptiness and despair are constant.
Other symptoms that suggest depression, not just grief, include:
- Intense, pervasive sense of guilt.
- Thoughts of suicide or a preoccupation with dying.
- Feelings of hopelessness or worthlessness.
- Slow speech and body movements.
- Inability to function at home, work, or school.
- Seeing or hearing things that aren’t there.
Finding professional help
If you’re experiencing symptoms of complicated grief, trauma, or clinical depression, talk to a mental health professional right away. Left untreated, these conditions can lead to significant emotional damage, life-threatening health problems, and even suicide. But treatment can help you get better.